Perichondritis: What is it & what are the symptoms and treatments?
Perichondritis: What is it & what are the symptoms and treatments?
10 min
Published December 22, 2025
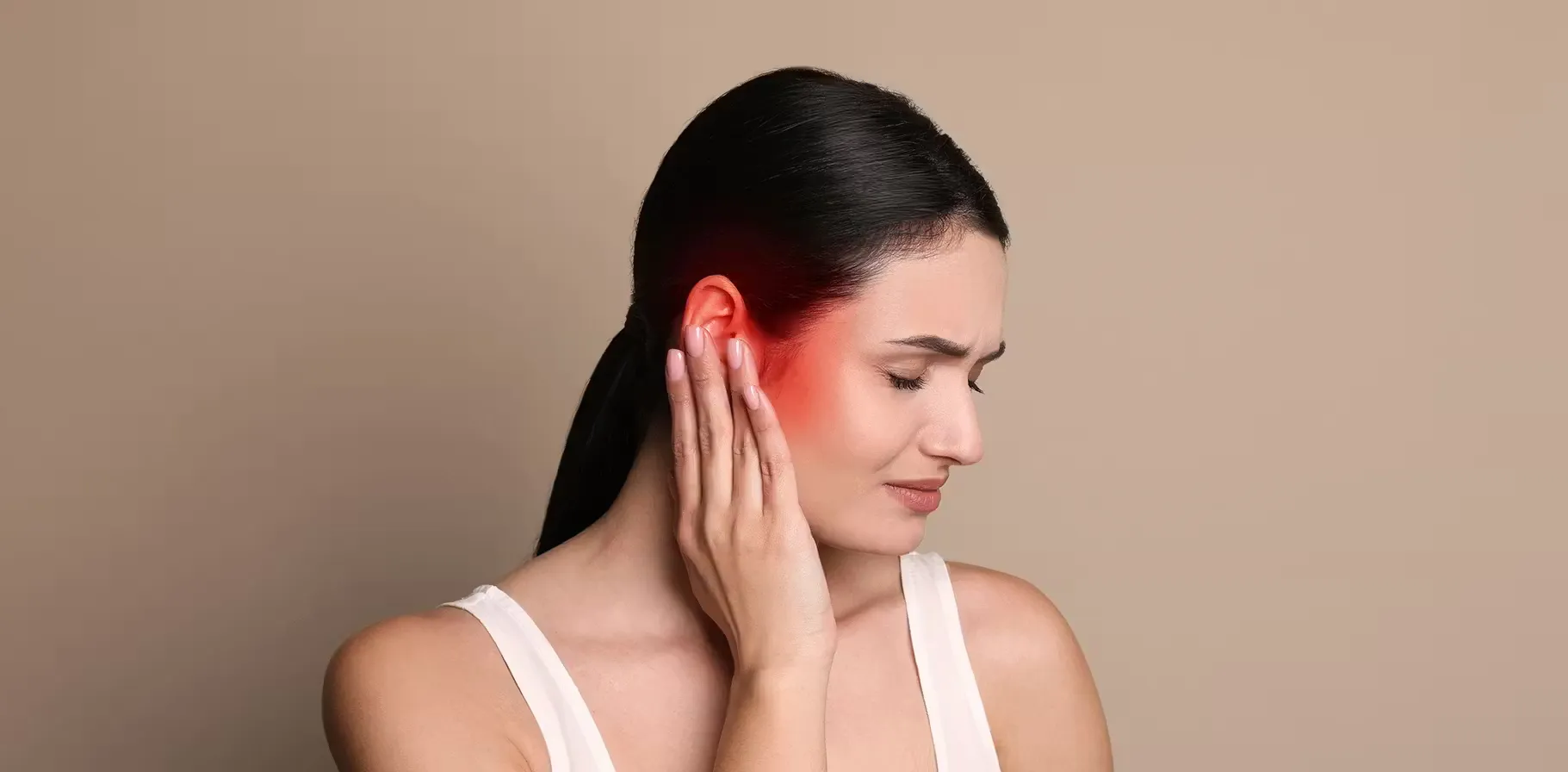
Perichondritis is an inflammation of the tissue covering the cartilage of the outer ear - how does that affect your hearing?
Perichondritis is also closely related to 'cauliflower ear', a deformity of the ear found commonly among boxers, wrestlers, rugby players and martial artists.
What are the Symptoms of Perichondritis?
When the outer ear becomes sensitive to touch, often red and inflamed, you may be experiencing perichondritis and is often accompanied by these symptoms:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Redness around the outer ear
- Skin in the area feels warm to the touch
It typically affects the top of the ear rather than the earlobe. These symptoms can be quite uncomfortable and can develop suddenly or gradually.
The duration of symptoms in perichondritis may vary greatly. For those with acute cases, symptoms such as pain and swelling can resolve within a few weeks to a few months. However, if the condition is chronic or not properly managed, symptoms can last much longer.
Chronic cases can lead to complications, such as:
- Deformities of the outer ear
- Persistent discomfort which can significantly affect an individual's quality of life¹.
What Causes Perichondritis?
There are several common causes of perichondritis:
How is Perichondritis Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of perichondritis mainly involves a clinical examination by a health professional. During the visit, a doctor will look for signs such as swelling, redness, pain, and any history of trauma or previous surgery to the ear. Although the physical exam is key, additional tests can be done, such as image studies, to exclude other potential conditions that could imitate the symptoms of perichondritis. For example, if there is concern about an abscess or a more severe underlying problem, an ultrasound or computerized tomography can be used.
What is the Risk of Untreated Perichondritis?
It is essential to diagnose perichondritis early, since neglecting the condition can lead to more significant problems, such as necrosis of the ear tissue. This occurs when the swelling gets so severe that it cuts off the blood supply to your cartilage, destroying it and leading to tissue death. A specific example of the deformation that can occur in chronic cases is similar to what is observed in Winkler's disease, a condition that also leads to an abnormal ear shape and associated discomfort³ and is characterized by tissue necrosis.
Chronic perichondritis can lead to serious complications, including ear deformity, such as in cauliflower ear. This can occur when there is repeated trauma to the ear leading to swelling and fibrosis and changing the shape of the ear permanently.
Both conditions, cauliflower ear and Winkler's disease, require careful management to avoid deformities of the ear, especially in athletes involved in contact sports⁴.
How is Perichondritis Treated?
References
¹ Krogmann, R. J., Jamal, Z., & King, K. C. (2018). Auricular Hematoma. https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk531499
² Moutsopoulos, H. M., & Zampeli, E. (2020). The Skin, the Eyes, and the Ears in Rheumatic Diseases. In Immunology and Rheumatology in Questions (pp. 155-165). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-56670-8_10
³ Subhadarshani, S., Gupta, V., Chahal, A., & Verma, K. K. (2017). Saddle-nose and bilateral cauliflower ear deformities with pyoderma gangrenosum-like ulcers, cavitary pulmonary lesions, digital gangrene and pulselessness in a young female. Case Reports, 2017, bcr-2017. https://casereports.bmj.com/content/2017/bcr-2017-220434.short
⁴ Patil, S. (2017). A Clinical Study of Benign Lesions of Pinna (Master's thesis, Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences (India)). https://search.proquest.com/openview/03c102a70ec09dc9bc12e4f74abc024a/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=2026366&diss=y




